The Natural Resources Center acquired Masinotek's environmental measurements and services for the climate project
 Peat fields account for more than half of Finland's agricultural greenhouse gas emissions. In its four-year project, Finland's Natural Resources Center, LUKE, is investigating the variability of the groundwater level in peat fields and its significance for carbon dioxide emissions of the peat field. During the summer and autumn of 2021, Masinotek will supply several dozen continuous IoT measuring stations and sensors to the project. Our company is also responsible for the field installation of the equipment, data collection and delivery of the data system, as well as maintenance for the Natural Resources Center.
Peat fields account for more than half of Finland's agricultural greenhouse gas emissions. In its four-year project, Finland's Natural Resources Center, LUKE, is investigating the variability of the groundwater level in peat fields and its significance for carbon dioxide emissions of the peat field. During the summer and autumn of 2021, Masinotek will supply several dozen continuous IoT measuring stations and sensors to the project. Our company is also responsible for the field installation of the equipment, data collection and delivery of the data system, as well as maintenance for the Natural Resources Center.
Groundwater monitoring and soil moisture measuring stations from Masinotek
 The Natural Resources Center project (https://www.luke.fi/en/projektit/vesihiisi/) investigates the generation and management of greenhouse gases formed during the decomposition of peat and accelerating climate change. The project investigates the reduction of carbon emissions from a peat field through field water management. The idea is to be able to minimize the amount of carbon dioxide transferred from the peat field to the atmosphere and watershed. The method in managing the water levels is the continuous accurate measurement and control of the groundwater level. The aim is that too much water does not interfere with cultivation, but on the other hand the amount of water remains high enough to slow down the decomposition of peat as much as possible.
The Natural Resources Center project (https://www.luke.fi/en/projektit/vesihiisi/) investigates the generation and management of greenhouse gases formed during the decomposition of peat and accelerating climate change. The project investigates the reduction of carbon emissions from a peat field through field water management. The idea is to be able to minimize the amount of carbon dioxide transferred from the peat field to the atmosphere and watershed. The method in managing the water levels is the continuous accurate measurement and control of the groundwater level. The aim is that too much water does not interfere with cultivation, but on the other hand the amount of water remains high enough to slow down the decomposition of peat as much as possible.
In the project, the most significant part of Masinotek's equipment deliveries is the assembly and delivery of automatic groundwater measuring stations to a research area of approximately ten hectares. In addition to these, our company has built a network of soil moisture measuring stations on the peat field, the data of which are also collected continuously.

Continuous measurement of soil moisture and groundwater
Soil moisture is monitored in the area from several different survey plots, and at each terrain point, sensors supplied and installed by Masinotek measure soil temperature and humidity from three different depths. The sensors are connected to data loggers equipped with a modem, which also distribute electricity to the sensors. Data loggers run on long-life Lithium batteries and can measure and transmit data in real time for several years without battery replacement.
The LoRaWAN wireless local area network is also available from Masinotek
Arable farming is practiced in the study area, and therefore all measuring stations must be able to send measurement data wirelessly. As an exceptional number of measuring stations were installed in the same area, with a total of more than 70 observation points, Masinotek decided to build its own local network based on LoRa technology. The company implemented this as part of an overall project, and as a result, the research area now has a wireless data transmission network in accordance with the LoRaWAN standard, which can collect data from thousands of different measuring sensors within a range of about 2 km. The measurement data is first sent from the measurement points via the LoRa local area network implemented by Masinotek to a LoRa base station located in the field, from where it is then automatically sent via a 4G connection to Masinotek's servers.
Data monitoring and analysis by EMMI software
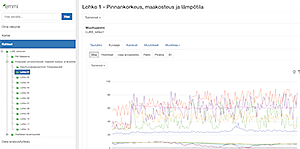
EMMI data monitoring ground moisture and groundwater levels in Masinotek's delivery package includes the responsibility of the measuring station for the continuous transmission, storage, analysis and delivery of data for use by researchers at the Natural Resources Center. All of this was accomplished with an Internet-based EMMI monitoring system developed by Masinotek. Each measurement station has its own observation points in the system, where photographs, documents, raw data from field measuring devices and the necessary derived results calculated from the data can be displayed. The EMMI system automatically receives and processes measurement messages via various interfaces (APIs). EMMI also uses preset thresholds to automatically check the results and correct any incorrect data.
Masinotek involved in combating climate change
As a whole, the Luke peat field project is one of Finland's most significant projects to study and combat the climate impact of agriculture. For Masinotek, the project is important, as significant efforts will be made to monitor the climate impact of agriculture throughout the EU in the coming years. Masinotek's constantly evolving EMMI system rises to the challenge in collecting and analyzing data from various measurement data. Reducing emissions that are harmful to the climate and at the same time maintaining good operating conditions of Finnish agriculture is an important goal for auothorites. Masinotek is pleased to be involved in this important work.

 LOGIN
LOGIN